■ Example of research topics ■
[ Solar ]
1. 4 junction by wafer bonding /
2. High-speed MOVPE /
3. EL and PL characterization /
4. Thin-film multi-junction (design and light trapping) /
5. 1.15 eV middle cell with MQWs /
6. Theoretical modeling of MQWs (quasi bulk approach and cell design) /
7. WoW /
8. ELO /
9. Dilute nitride MQW
[ Growth ]
1. III-V on Si photo detector /
2. III-V on Si solar cell
[ LED ]
1. Chip-white LED
[ Solar Fuel ]
1. CPV + water electrolysis /
2. CO2 reduction /
3. Semiconductor/electrolyte interface /
4. Polarization-controlled nitride photocathode /
5. Design of energy management system using hydrogen-based power storage
[ Quantum Modeling ]
1. Quantum modeling of insulators
Substrate reuse with Epitaxial Lift-Off for low-cost solar cell applications
T. Nakata, N. Miyashita (Okada Lab.), K. Watanabe, H. Sodabanlu, and M. Sugiyama, Y. Okada (Okada Lab.)
The III-V compound semiconductors have an advantage of integrating the multi-junction solar cells yielding record efficiencies. However, these high efficiency solar cells have not been used for terrestrial applications because of the high material cost. After the epitaxial crystal growth, only the device layer is necessary for a solar cell, and hence by reusing the expensive substrates we can achieve cost reduction. The epitaxial lift-off (ELO) is known as a major substrate reuse method. The ELO process is based on the selective etching of an AlAs release layer, which enables the lift-off of a thin film solar cell and the reuse of the substrate. In this research, we are investigating the separation process, the device fabrication process and the substrate cleaning process for the industrial application of the substrate reuse.
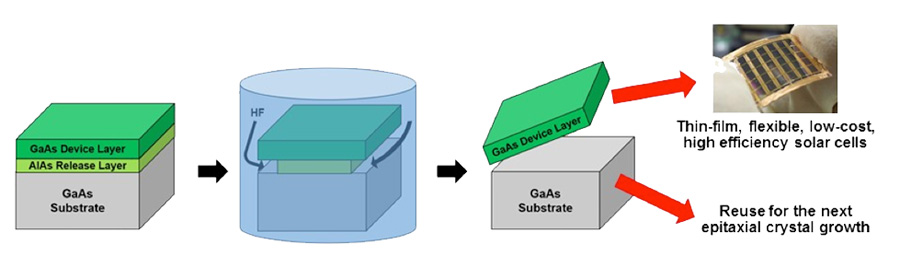
Fig. Concept of Epitaxial Lift-off (ELO).